The Excel Master [TEM]
Collaborative Excel: Harnessing the Power of Collaboration Features
Mastering Time: Working with Date and Time Data in Excel
Unleash the Power of Text Splitting in Excel
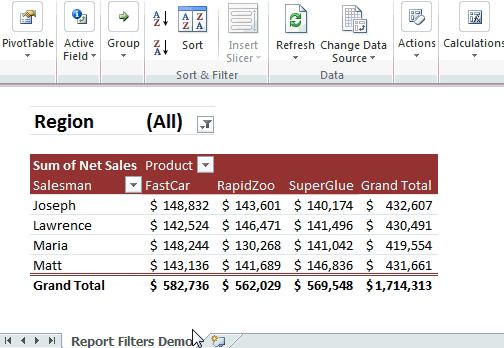
Mastering Excel Pivot Tables and Charts: Your Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the Excel Interface: A Beginner's Guide
Excel Shortcuts Guide: Boost Your Productivity with Handy Keyboard Shortcuts
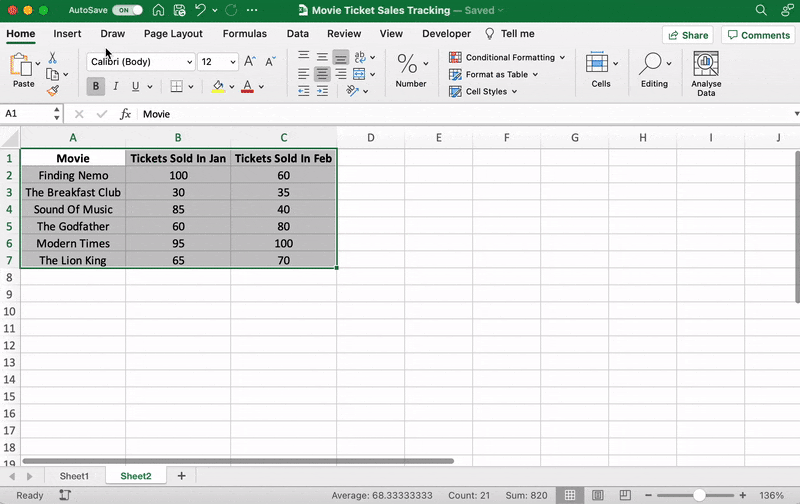
Mastering Excel: Tips and Tricks for Efficient Data Management
Unveiling Data Insights: A Practical Guide to Excel Data Analysis
Day 10: Excel Mastery Reflection and Beyond
Congratulations! You've reached the final day of your "Master Excel in 10 Days" journey. Over the past nine days, you've immersed yourself in the world of Excel, from the basics to advanced techniques. Today, we'll reflect on your journey, celebrate your accomplishments, and explore the endless possibilities that lie ahead.
Reflecting on Your Excel Mastery:
Take a moment to appreciate how far you've come. You started with Excel's fundamental tools, gradually building your skills to tackle complex challenges, analyze data, and craft compelling visualizations. Your dedication and commitment have transformed you into an Excel enthusiast.
Your Accomplishments:
Day 1: You embraced the Excel basics and learned to navigate the interface.
Day 2: You dived into formatting fonts, colors, and sizes to make your spreadsheets visually appealing.
Day 3: You explored cell styles, unleashing creativity with pre-designed formats.
Day 4: You harnessed the power of conditional formatting to highlight important insights.
Day 5: You discovered the world of borders and gridlines, giving structure to your data.
Day 6: You ventured into custom number formats, mastering data representation.
Day 7: You unlocked Excel's functions, turning numbers into insights.
Day 8: You solved real-world problems using data analysis tools.
Day 9: You became a data visualization maestro, crafting engaging visual stories.
Excel Beyond the 10 Days:
As you conclude this journey, remember that Excel is a dynamic tool with boundless possibilities. Your newfound skills can be applied across industries, from finance and marketing to healthcare and education. Here's what lies ahead:
Advanced Functions: Dive deeper into Excel's functions, from INDEX/MATCH to complex array formulas.
Power Query and Power Pivot: Explore data transformation and modeling for more in-depth analysis.
VBA and Macros: Learn automation through Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) to boost efficiency.
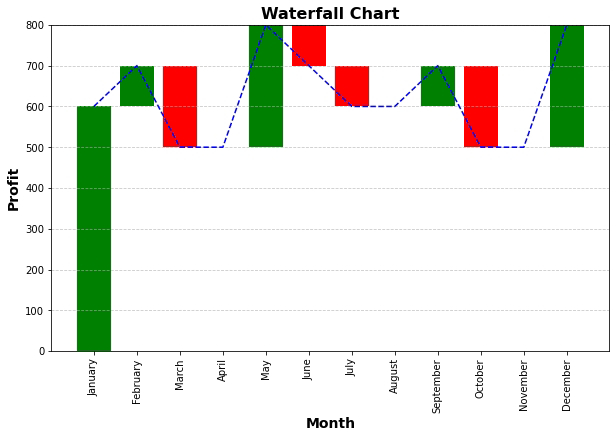
Advanced Charts: Experiment with advanced charts like histograms, pareto charts, and radar charts.
PivotTables and PivotCharts: Master these tools for multidimensional analysis and reporting.
Machine Learning: Integrate Excel with machine learning tools for predictive analytics.
Your Excel Journey Continues:
Your journey doesn't end here—it's just the beginning. Excel is a versatile tool that adapts to your growth and curiosity. Whether you're a business analyst, student, researcher, or entrepreneur, Excel will be your ally in unlocking insights and making informed decisions.
Thank you for embarking on this "Master Excel in 10 Days" adventure with us. We hope you've gained valuable skills and the confidence to excel in your professional and personal endeavors. Keep exploring, keep learning, and keep excelling!
Day 9: Advanced Data Visualization - Crafting Engaging Visual Stories
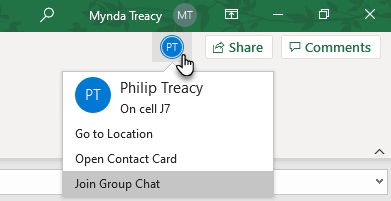
Collaborative Excel: Harnessing the Power of Collaboration Features
Real-Time Co-Authoring Section 1: Enabling Real-Time Co-Authoring - *How to set up co-authoring in Excel:* To enable co-authorin...