Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet software used for various tasks, from simple data entry to complex data analysis. To harness its capabilities effectively, it's crucial to understand the Excel interface and navigation. In this guide, we'll walk you through the key elements of the Excel interface and how to navigate them.
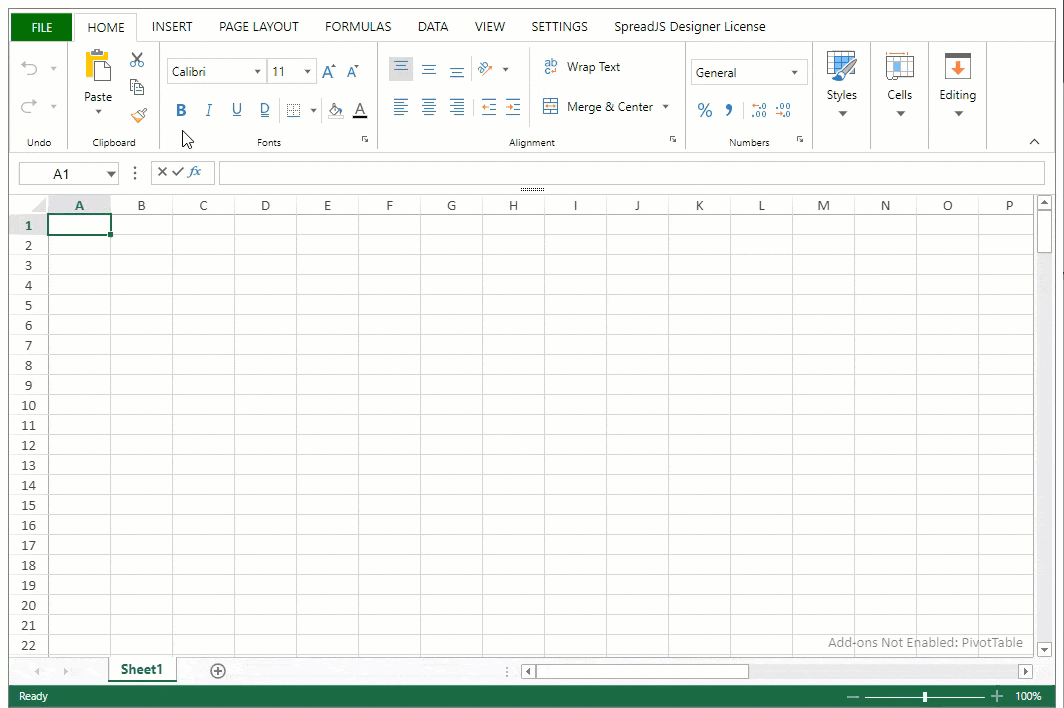
The Excel Interface:
1. Workbook:
- Excel documents are called workbooks.
- Each workbook can contain multiple worksheets.
- By default, a new workbook opens with three blank worksheets labeled Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3.
2. Ribbon:
- The Ribbon is the horizontal toolbar at the top of the Excel window.
- It contains tabs like Home, Insert, Page Layout, Formulas, Data, Review, and View.
- Each tab has groups of related commands and functions.
3. Quick Access Toolbar:
- Located above the Ribbon, it provides easy access to commonly used commands.
- You can customize it to add your favorite commands.
4. Formula Bar:
- Just below the Ribbon, the Formula Bar displays the contents of the active cell.
- You can use it to enter or edit data and formulas.
5. Name Box:
- The Name Box, to the left of the Formula Bar, displays the address or name of the active cell.
- You can use it to quickly navigate to specific cells.
6. Worksheet Tabs:
- At the bottom of the Excel window, you'll find worksheet tabs.
- Click on a tab to switch between worksheets in the same workbook.
Navigation in Excel:
1. Moving Around Cells:
- Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to move up, down, left, or right within a worksheet.
- To quickly move to the beginning or end of a data region, press `Ctrl` + an arrow key.
2. Scrolling:
- To scroll vertically, use the mouse wheel or the scrollbar on the right.
- To scroll horizontally, use the scrollbar at the bottom.
3. Selecting Cells:
- Click on a cell to select it.
- To select a range of cells, click and drag the cursor over the desired cells.
4. Navigating Worksheets:
- Click on a worksheet tab to switch between worksheets.
- Use `Ctrl` + `Page Up` or `Ctrl` + `Page Down` to move between worksheets in a workbook.
5. Go To:
- To quickly move to a specific cell, press `Ctrl` + `G` to open the Go To dialog box.
- Enter the cell reference and click OK.
6. Splitting Panes:
- You can split the worksheet into multiple panes to view different parts simultaneously.
- Go to the View tab and click Split.
Conclusion:
Understanding the Excel interface and mastering navigation is the foundation for effective spreadsheet work. As you become familiar with these elements and shortcuts, you'll find yourself working more efficiently and confidently in Excel. Whether you're managing data, creating charts, or performing complex calculations, knowing your way around Excel is a valuable skill.







No comments:
Post a Comment